Tax Research Insights
Welcome! This site shares posts written by authors of the Department’s annual research reports. The researchers highlight interesting findings from the reports they produce. Each post focuses on a key idea from their research.
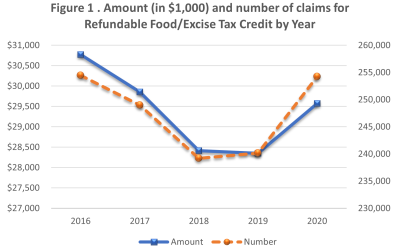
More people claimed the Refundable Food/Excise Tax Credit during the 2020 Pandemic
Hawaii has several tax credits that promote social welfare. More people claimed these credits during the Covid-19 pandemic, supporting the idea that these credits provide important economic support when Hawaii’s families are hurting the most. More Hawaii taxpayers...
What would recession do to Hawaii’s Tax Revenues?
There has been significant talk of a recession in the financial press. High levels of inflation have prompted the Federal Reserve (Fed) to take decisive action by raising the benchmark interest rates. Will the abrupt change in monetary policy cause a recession? And if...
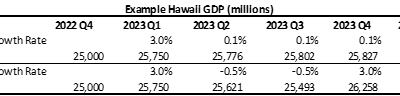
The impacts of tax credit diminish over time if the income limitation is not updated
Social welfare tax credits often have an income-based limitation. What happens when income limits remain unchanged for long periods of time? Let’s look at two examples here Tax credit for Low-Income Household Renters. The tax credit is computed by multiplying $50 by...
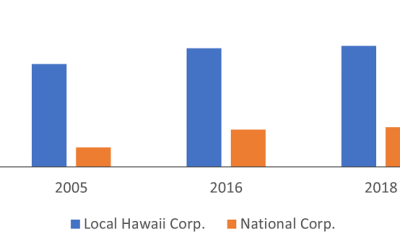
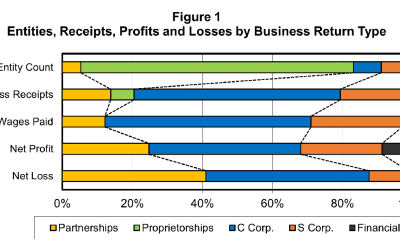
While fewer in number, national corporations generate the lion’s share of receipts in the State
Corporations are the main contributors of Hawaii business receipts. In tax year of 2019, corporations contributed 78% of Hawaii business receipts. There are two types of corporations: those operating only in the State of Hawaii and those that operate nationally (i.e....
Hawaii’s individual income tax is progressive
Higher income groups pay more in taxes relative to their income in Hawaii. A progressive tax structure is defined as one where higher income taxpayers pay a larger percentage of their income in taxes. By this metric, Hawaii’s individual income tax is clearly...
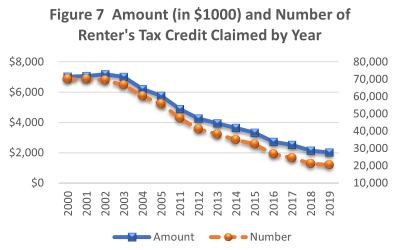
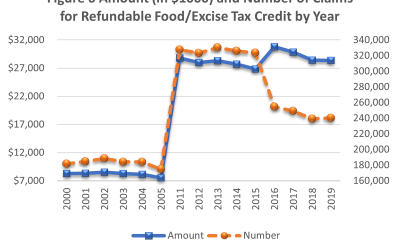
Increasing incomes mean fewer people claim the Food/Excise Tax Credit over time
The Food/Excise Tax Credit is the largest tax credit in the State promoting social welfare. In the 2019, there were 240,158 claims worth $28.4 million. Figure 6, Tax Credits Claimed by Hawaii Taxpayers (copied below), shows how the credit has evolved overtime. The...
C corporations represent the smallest number of businesses yet produce most of the State’s business receipts
A business is classified by its entity size Businesses can legally organize themselves in different ways. C corporations have more flexibility in their activities, but they are required to pay corporate income tax. S corporations and partnerships are pass-through...
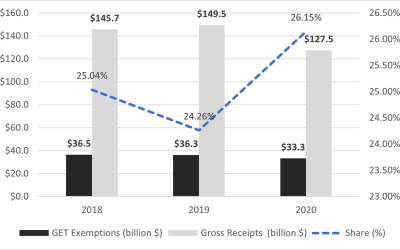
A quarter of all gross receipts in Hawaii are exempted from the GET
The top five exemptions account for 60% of all exemptions claimed. The General Excise & Use Tax (GET), which is a very broad gross receipts tax, is the largest tax type in Hawaii. GET is a tax on income from almost all business activities, including wholesaling,...
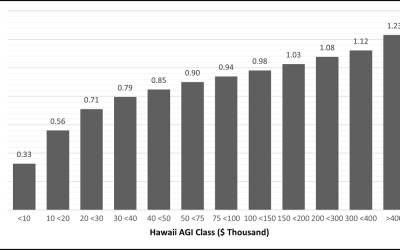
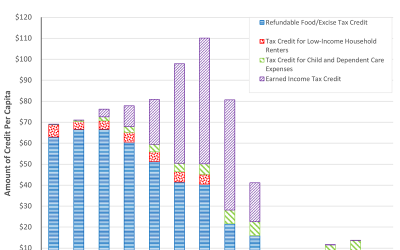
Who benefits most from Hawaii’s Tax Credits?
This post highlights some interesting trends that emerged in the 2019 Report Tax Credits Claimed by Hawaii Taxpayers. Figure 5 from the report (see below) shows how welfare enhancing tax credits varies by income and some interesting results emerge: The Refundable...